Lesson Plans & Activities
Voices of Resilience: Collecting Stories of Survivors
This lesson is best used as part of the HEART Force curricular unit, but it can also be used as part of a unit on natural hazards.
Students collect stories from community members about their experiences with hazards.
Adapting to Extremes: Exploring the Science of Drought in Colorado
This lesson is best taught at the beginning of a HEART Force unit, but it can also act as a stand-alone lesson to introduce students to drought in Colorado.
Humans have been affected by severe drought throughout history; in this lesson students explore this concept by analyzing environmental data to classify patterns and practice communicating their findings.
Data Puzzle: Windstorms on the Front Range
Although strong windstorms are a common weather event at the foot of the Rocky Mountains, a record-breaking windy spring soon after the Marshall Fire disaster had the public feeling on-edge. In this Data Puzzle, students analyze data on the number of windstorms and the number of red flag warnings to investigate the question, “Is it getting windier on the Front Range as the climate warms?”
Data Puzzle: Snow in the Rockies
Water from snowmelt high in the Rocky Mountains feeds into the Colorado River, a river system that more than 40 million people rely on for water. In this Data Puzzle, students analyze snowfall and snowmelt datasets to investigate the question, "How have snow conditions in the East River Watershed changed over time?"
Data Puzzle: Wildfire, Drought, and the Future of Forests
This data puzzle is a stand-alone lesson that is part of a larger collection of data puzzles.
Wildfires are burning more and more of the forests across the western United States. In this Data Puzzle, Data Puzzle, students analyze post-fire forest recovery datasets as they gather evidence to construct explanatory models for the following question, "How do climate conditions impact the recovery of forests after a wildfire?"
Social Vulnerability to Natural Hazards
This is the third of four lessons in the Lake County Cascading Hazards unit. This lesson can also be used in the HEART Force Curriculum.
In the third lesson of the Lake County Cascading Hazards unit, students learn about social factors that might make one group more vulnerable to a hazard than another.
Lake County Cascading Hazards Unit
The unit has four lessons in total.
This unit builds an understanding of five natural hazards and their connections in the context of place-based community resilience.Take Action
Actions that will help families prepare for the next disaster can take a few minutes, and make a big difference when the time comes. Students will create a social media post or a short video to share what they are doing to prepare and encourage their friends to be prepared too.
In the last lesson of the Lake County unit, students develop ideas to increase resilience to hazards in their community.Cascading Hazards
This is the second of four lessons in the Lake County Cascading Hazards unit.
In the second lesson of the Lake County Cascading Hazards unit, students dig into local stories and datasets, and learn about the connections between natural hazards.ReVisioning Hazards
This is the first lesson in the Lake County Cascading Hazards unit, but can be used for any introduction to natural hazards curriculum.
In the first lesson of the Lake County Cascading Hazards Unit, students read a poem written by a local fire survivor, and utilize a visualization practice to build personal resilience.HEART Force Wildfire Resilience Game
This lesson is best used after the wildfire hazard lesson in the HEART Force curricular unit, for students to apply their learning and recover from a hypothetical wildfire in their own community.
In this scenario-based role-play game, students play the role of community members planning for wildfire resilience in their community. After a wildfire occurs, they see how resilience and recovery efforts pan out in their hometown based on their planning efforts.
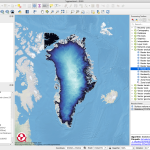
From Greenland to our Coasts: Exploring Sea Level Change with QGreenland
This unit consists of 3 lessons, each tied to NGSS life science standards
In this unit, students will explore how the Greenland Ice Sheet is changing and why that affects coastal communities worldwide. Students will view authentic Greenland geospatial data and learn how to create flood maps to assess local risk in QGIS.
High School Drought Unit
This HEART Force curricular unit includes all lessons for the High School Drought curriculum.
The HEART Force curriculum builds an understanding of fire, flood, or drought in the context of place-based community resilience.
High School Flood Unit
This HEART Force curricular unit includes all lessons for the High School Flood curriculum.
The HEART Force curriculum builds an understanding of wildfire, flood, or drought in the context of place-based community resilience.
High School Wildfire Unit
This HEART Force curricular unit includes all lessons for the High School Wildfire curriculum.
The HEART Force Curriculum builds an understanding of wildfire, flood, or drought in the context of place-based community resilience.
Middle School Drought Unit
This HEART Force curricular unit includes all lessons for the Middle School Drought curriculum.
The HEART Force curriculum builds an understanding of wildfire, flood, or drought in the context of place-based community resilience.
Middle School Wildfire Unit
This HEART Force curricular unit includes all lessons for the Middle School Wildfire curriculum.
The HEART Force curriculum builds an understanding of wildfire, flood, or drought in the context of place-based community resilience.
Middle School Flood Unit
This HEART Force curricular unit includes all lessons for the Middle School Flood curriculum.
The HEART Force curriculum builds an understanding of wildfire, flood, or drought in the context of place-based community resilience.
Data Puzzle: Megadrought in the Colorado River Basin
This data puzzle is a stand-alone lesson that is part of a larger collection of data puzzles.
Much of the western United States is experiencing drought conditions. In this Data Puzzle, students analyze authentic climate data to construct explanatory models for the following question, "What is causing the megadrought in the Colorado River Basin?"
Data Puzzle: Megafire - Rare Occurrences or the New Normal?
This data puzzle is a stand-alone lesson that is part of a larger collection of data puzzles.
Megafires have been a hot topic in the news over the past few years, but are they a new phenomenon? In this Data Puzzle, students analyze authentic wildfire data to construct explanatory models for the follow question, "How and why has the number of megafires have changed over time?"
The Future of Forests
This storyline unit consists of 9 lessons, each tied to NGSS life science standards
In this middle school unit supported by NASA, students engage with online interactives, authentic datasets, and citizen science protocols to construct models and explanations for the unit driving question, "How do landscapes recover after a wildfire?"We are Water Kahoot Trivia - Advanced Level
Answer some fun trivia questions about the science of water and the geography of the Four Corners Region! Pick a level where you want to start and see how far you can go!
Challenge your students with advanced level trivia from We are Water about the science of water and the geography of the Four Corners Region.
We are Water Kahoot Trivia - Intermediate Level
Answer some fun trivia questions about the science of water and the geography of the Four Corners Region! Pick a level where you want to start and see how far you can go!
Challenge your students with intermediate level trivia from We are Water about the science of water and the geography of the Four Corners Region.
We are Water Kahoot Trivia - Beginner Level
Answer some fun trivia questions about the science of water and the geography of the Four Corners Region! Pick a level where you want to start and see how far you can go!
Challenge your students with beginner level trivia from We are Water about the science of water and the geography of the Four Corners Region.
HEART Force Curriculum Overview
This unit consists of several lessons and can take anywhere from 1 to 6 weeks to teach, depending on which lesson teacher choose to incorporate.
The HEART Force curriculum builds understanding of wildfire, flood, or drought in the context of place-based community resilience.
Communicate Existing Plans
This is a guide that can be used for a pathway for the Community Resilience Expo.
In this sub-unit, students will learn more about their community’s resilience plans, choose a specific topic to focus on, and develop a product to communicate the plan to their peers and/or their community.
Adapting to Extremes: Exploring the Science of Wildfire in Colorado
This lesson is best used as part of the HEART Force curricular unit, but it can also act as a stand-alone lesson to introduce students to wildfire in Colorado.
Students build an understanding of wildfire in Colorado using multiple data sources in a jigsaw format.
Adapting to Extremes: Exploring the Science of Floods in Colorado
This lesson is best taught at the beginning of a HEART Force unit, but it can also act as a stand-alone lesson to introduce students to floods in Colorado.
The way we choose to design our communities has impacted community risk and vulnerability to flooding; in this lesson, students will explore this concept by analyzing environmental data to classify patterns and practice communicating their findings.
HEART Force Flood Response Game
This lesson is best used after the Colorado Flood lessons in the HEART Force curricular unit, for students to apply their learning and respond to a hypothetical flood in their own community.
This interactive game has students work in three “zone response teams” to solve community challenges that arise during the course of an extreme flooding event by using available individual and community resources.
The Vocabulary of Hazards
We suggest teaching this lesson to introduce the unit as it will benefit students in their understanding of natural hazards throughout the entire HEART Force Unit.
This lesson uses a matching game to build students' understanding and familiarity with different terms used in the world of resiliency planning.
Envisioning a Resilient Future
We suggest teaching this lesson to introduce the HEART Force Unit.
In this lesson, students create a vision for the future of their community and identify what resources are most important to them as a starting point for resilience planning.
A Changing Climate: Understanding Floods in Colorado
This lesson is best taught at the beginning of a HEART Force unit, but it can also act as a stand-alone lesson to introduce students to floods in Colorado.
Students build an understanding of flooding in Colorado using multiple data sources in a jigsaw format.
A Changing Climate: Understanding Wildfire in Colorado
This lesson is best used as part of the HEART Force curricular unit, but it can also act as a stand-alone lesson to introduce students to wildfire in Colorado.
Students build an understanding of wildfire in Colorado using multiple data sources in a jigsaw format.
Hourglass Lake Fire Challenge - El reto del incendio del lago Hourglass
This lesson is best used after the wildfire hazard lesson in the HEART Force curricular unit, for students to apply their learning and respond to a hypothetical wildfire in their own community.
In this interactive game, students work in three “zone response teams” to solve community challenges that arise during the course of a wildfire event by using available individual and community resources.
HEART Force Drought Game
This lesson is best used after the Colorado Drought lessons in the HEART Force curricular unit, for students to apply their learning and respond to a hypothetical drought in their own community.
In this interactive game, students work in three "resilience teams" to solve community challenges that arise during the course of an extreme drought event by using available individual and community resources.
Flood Resilience in Colorado StoryMap
This is a lesson that can be used to get ideas and prepare for the Community Resilience Expo.
Students interact with a flood StoryMap to explore the Colorado Resiliency Framework.
Wildfire Resilience in Colorado StoryMap
This is a lesson that can be used to get ideas and prepare for the Community Resilience Expo.
Students interact with a wildfire StoryMap to explore the Colorado Resiliency Framework.
Exploring Local Hazard Mitigation Plans
This lesson is part of the Community Resilience Expo, a culminating event for the HEART Force curriculum unit, where students will share what they’ve learned during the hazard lesson and the role-playing game.
In this lesson, students will explore their county Hazard Mitigation Plan to gain understanding about the hazard in their area (flooding, wildfire, or drought), including historic hazards, probability of future occurrences of the hazard, and vulnerability of the area to the hazard.
Design a Resilient Future
This is a lesson that can be used to get ideas and prepare for the Community Resilience Expo.
In this lesson, students will work in small groups to develop an idea to increase community resilience, utilizing Design Thinking.
A Changing Climate: Understanding Drought in Colorado
This lesson is best taught at the beginning of a HEART Force unit, but it can also act as a stand-alone lesson to introduce students to drought in Colorado.
Students build an understanding of drought in Colorado using multiple data sources in a jigsaw activity.